Foot and Ankle CT Scan
Ankle ct imaging the DFOV should be large enough to include the hindfoot which composed of “talus and calcaneus”, the midfoot “navicular, cuboid, and the cuneiforms” and at least the proximal bases of all five metatarsals. For most patients, it is possible to scan both ankles simultaneously within a 22cm DFOV, allowing a side by side comparison of the symptomatic ankle with the normal ankle.For the CT of the foot, the DFOV should be enlarged to include the entire forefoot “the metatarsals and phalanges” along with the hindfoot and midfoot.
CT images of the foot and ankle can be displayed in a number of different imaging plane. Some of these planes can be obtained directly by positioning the patient in a specific position, whereas planes are best displayed by reformatting the data. The choice of which plane to display depends on which joint is of primary concern.
For the foot, the axial plane is defined as the plane parallel to the plantar surface of the foot. This plane is acquired directly when the patient is positioned so that the toes are pointing straight up.
 |
| When the patient is positioned with the toes pointing straight up, data are acquired in the direct axial plane. |
The patient is positioned with bended knees so that it’s feet lies flat on the ct scan table data are collected directly in the oblique coronal plane. The gantry is then tilted, usually 20 to 30 degrees this gantry position, the top of the gantry should go away from the patient so the scan plane is perpendicular to the subtalar joint.
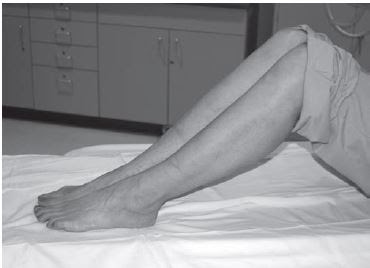 |
| When the patient is positioned with knees bent, feet flat on the scan table, and the gantry is angled perpendicular to the subtalar joint, data are acquired directly in the oblique coronal plane |
Foot and Ankle- CT Imaging Anatomy
Computed tomography data of the foot and ankle can be obtained in a number of different imaging planes. The choice of plane depends on which aspect is of primary concern. Like for example in the foot, patients are most often positioned supine with legs on the table. Bringing the feet together or we may use a foot holder to help immobilize the motion of the foot during scanning.
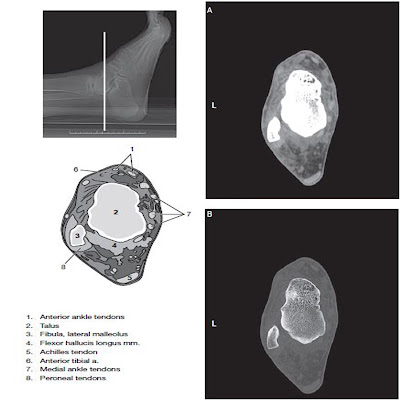 |
| Foot and Ankle CT Anatomy |
 |
| Foot and Ankle CT Anatomy |
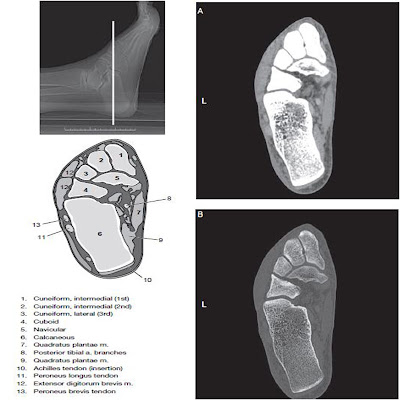 |
| Foot and Ankle CT Anatomy |








No comments:
Post a Comment