TUNNEL VIEW - PA Axial Projection
(1) CAMP COVENTRY METHOD
(2) HOLMBLAD METHOD (including variations)
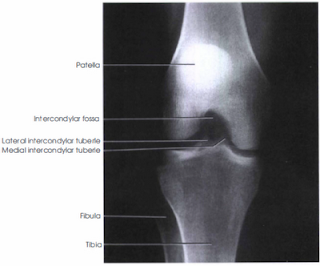
PA axial Projection of the knee best demonstrated the Intercondylar fossa, femoral condyles, tibial plateaus, and the intercondylar eminence are demonstrated and may show evidence of bony cartilaginous patology, osteochondral defects, or narrowing of the joint space.
 |
| Camp Coventry Method PA axial |
 |
| Holmblad Method |
Technical Factors:
Film size - 18 x 24 cm (8 x 10 inches), lenghtwiseMoving or stationary grid (or screen, <10 cm)
75 +- 5 kV range (increase 4 to 6 kV from PA knee)
mAs 5
Shielding:
Place lead shield over gonadal area. Secure around waist in kneeling position and extend shield down to midfemur level.Patient Position:
Camp Conventry Method - Take radiograph with patient prone; give pillow for head |
| Hoolmblad Variation |
Holmblad Variation - The patient is partially standing with affected leg on a stool or chair.
Radiographic Criteria:
Structure Shown:The intercondylar fossa, articular facets (tibia plateaus), and knee joint space are demonstrated clearly.
Position:
 |
| Holmblad Variation (on Stool) |
No rotation will be evidenced by the symmetric appearance of the distal posterior femoral condyles and superimposition of approximately half of fibular head by tibia.
Articular facets and intercondylar eminence of tibia should be well visualized without superimposition.
Collimation and CR:
Center of four-sided collimation field should be to mid-knee joint area.
Exposure Criteria:
Optimal exposure should visualized soft tissue in the knee joint space and an outline of the patella through the femur.
Trabecular markings of femoral condyles and proximal tibia appear clear and sharp, with no motion.
 |
| Knee Radiograph |
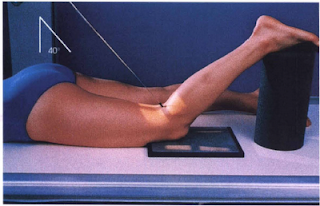
- Prone (Camp Coventry method):
Flex knee 40 to 50 degree; place support under ankle.
Center cassette to knee joint, considering projection of CR angle. - Kneeling ( Holmbad method):
- With patient kneeling on "all four," place cassette under affected knee and center IR to popliteal crease. Ask patient to support body weight primarily on opposite knee. Place padded support under ankle and leg of affected limb to reduce pressure on injured knee. Ask patient to slowly lean forward 20 to 30 degree, and hold that position (result in 60 to 70 degree knee flexion).
- Partially standing standdling table (Holmblad variation): Lower the exam table to a comfortable height for the patient, which is usually at the height of the knee joint. Ask patient to support body weight primarily on the unaffected knee. Place the effected knee over the Bucky of IR. Ask patient to slowly lean forward 20 to 30 degree and hold that position (results in 60 to 70 degree knee flexion.)
- Partially standing affected leg on stool or chair ( Holmblad variation ): Adjust the tool height to a comfortable height for the patient, which is usually at the height of the knee joint. Ask patient to support body weight primarily on the unaffected knee. Provide a step stool for support. Place the affected knee on the IR, while resting on the stool or chair. Ask patient to slowly lean forward 20 to 30 degree and hold that position (results in 60 to 70 degree knee flexion).
Central Ray:
1. Prone: Direct CR perpendicular to lower leg ( 40 to 50 degree caudad to match degree of flexion).
2. Kneeling: Direct CR perpendicular to IR and lower leg.
Direct CR to midpopliteal crease.
Minimum SID is 40 inches (100 cm)
Collimation:
Collimate on four sides to knee joint area.








No comments:
Post a Comment