- Any bony lessions involving the calcaneus, talus, and talocalcaneal joint will be shown and will demonstrate extend and alignment of fractures.
Technical Factors:
- IR size - 18 x 24 cm (8 x 10 inches)
- Divide in half, crosswise
- Detail screen
- Digital IR - use lead masking
- 60+- 5 kV range
- mAs 4
Shielding:
- Place lead shield over pelvic area to shield gonads.
Patient Position:
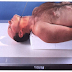
- Take radiograph with patient in the lateral recumbent position, affected side down. Give the patient a pillow for head. Flex of knee of affected limb about 45 degree; place opposite leg behind injured limb.
Part Position:
 |
| Lateral calcaneus |
- Center calcaneus to CR and to unmasked portion of IR, with long axis of foot parallel to plane of IR.
- Place support under knee and leg as needed to place plantar surface perpendicular to IR.
- Position ankle and foot for a true lateral, which places the lateral malleolus about 1 cm posterior to the medial melleolus.
- Dorsiflex foot so that plantar surface is at right angle to leg.
Central Ray:
- CR perpendicular to IR, directed to a point 1 inch (2.5 cm) inferior to medial malleolus.
- Minimum SID of 40 inches (100cm)
Collimation:
- Collimate to outer skin margins to include the ankle joint proximally and the entire calcaneus.
CR and DR:
- Close collimation and lead masking are important over unused portions of image plate to prevent fogging from scatter radiation to the hypersensitivity image plate or receptor.
Radiographic Criteria:
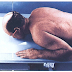
Structure Shown:
- Calcaneus is demonstrated in profile with the talus and distal tibia-fibula demonstrated superiorly, as well as the navicular and the open joint space of the calcaneus and cuboid distally.
 |
| Lateral Calcaneus |
Position:
- No rotation as evidenced by superimposition superior portions of the talus, open talocalcaneal joint, and lateral malleolus superimposed over the posterior half of the tibia and talus. Tarsal sinus and calcaneocuboidal joint space should appear open.
Collimation and CR:
- CR and the center of the collimation field should be about 1 inch (2.5 cm) distal to the tip of the lateral malleolus as seen through the talus.
- Four-sided collimation should include ankle joint proximally and talonavicular joint and base of fith metatarsal anteriorly.
Exposure Criteria:
- Optimal exposure will visualize some soft tissue and more dense portions of calcaneus and talus.
- The outline of the distal fibula should be faintly visible through the talus.
- Trabecular markings will appear clear and sharp, indicating no motion.






No comments:
Post a Comment